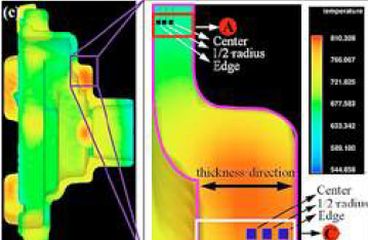
The segregation behavior of a rheological high pressure die-casting (Rheo-HPDC) AC46000 aluminum alloy at positions with different wall thicknesses was studied. The results reveal that positions with different wall thicknesses exhibit different cooling rates that can result in distinctly different segregation characteristics. Segregation results in varying microstructure, elemental distribution, and hardness along the thickness of an alloy.





